Inevitable

The world's governments face substantial issues as the working-age population shrinks, affecting economic development, social welfare systems, and pension schemes. To solve this, measures such as immigration expansion, assistance for working parents, investments in education and training, and flexible work arrangements must be enacted.
Fall in Working age population

Population expansion is unavoidable owing to a variety of factors such as medical and technological breakthroughs, greater sanitation, better nutrition, and more access to education. These factors have contributed to longer life expectancies and increased birth rates, resulting in a bigger global population.
Population Growth
Power to the individual

Millennials have grown up in a world of fast change and global issues, which has led them to seek meaning and purpose in their work and lives. This tendency is expected to continue as younger generations place a greater emphasis on social and environmental effect over conventional measurements of success.
Millennial Focus on Purpose

Technological advancements, automation, and globalization have resulted in a transformation in the conventional concept of work, with an increased focus on flexibility, creativity, and remote collaboration. This tendency is expected to continue as employment adapts to fit the requirements of a changing environment.
The Changing Notion of Work
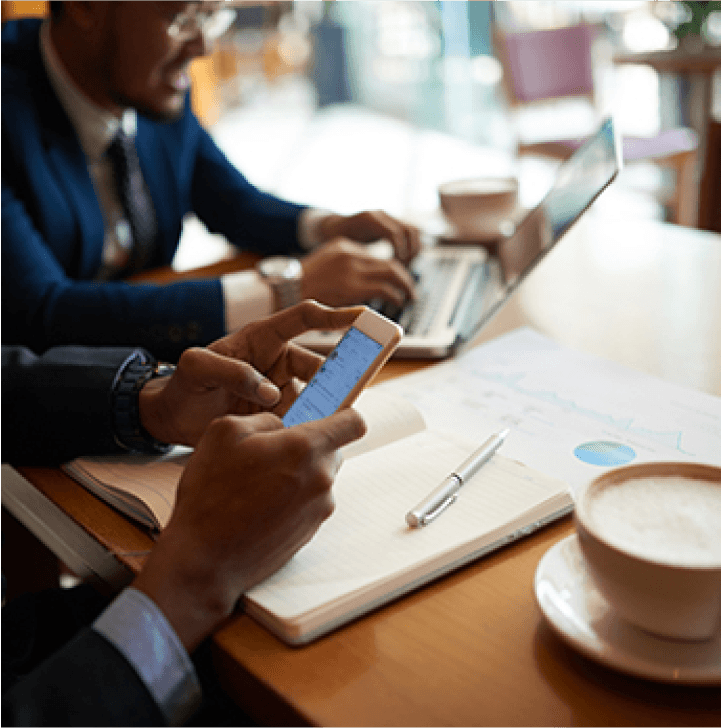

Several reasons are driving the increase of independent employees, including technology improvements, shifting views regarding work, and a desire for more flexibility and autonomy. This trend is expected to continue as more individuals seek alternative career opportunities and the gig economy expands.
The rise of independent workers
Rise of the crowd
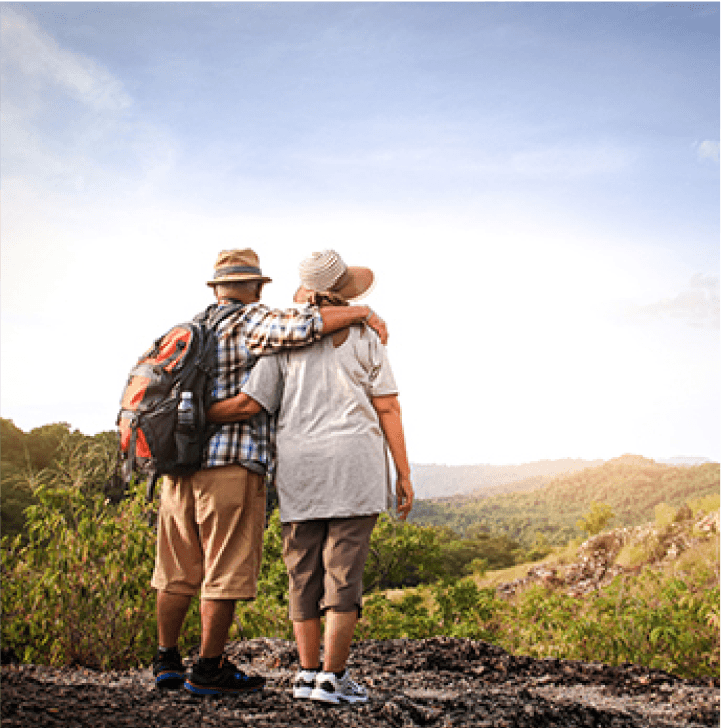

Retirement attitudes are changing as a result of a variety of circumstances, including greater life expectancy, changing economic situations, and altering attitudes about labor and leisure. This tendency is expected to continue in the future as more individuals seek innovative methods to combine their personal and work life.
Shifting views of Retirement
Ownership to access
Resource Scarcity

An aging population, increasing life expectancies, and changing family patterns are driving the increased need for elder care. As more individuals need assistance in their older years, this trend is expected to continue, posing new difficulties and possibilities for healthcare professionals, carers, and society as a whole.
Growing need for elder care

Several reasons are contributing to the reduction in fertility rates, including increasing access to family planning, changes in cultural standards, and more economic prospects for women. As more nations suffer demographic transitions and birth rates fall below replacement levels, this trend is expected to continue.
decline in fertility rates
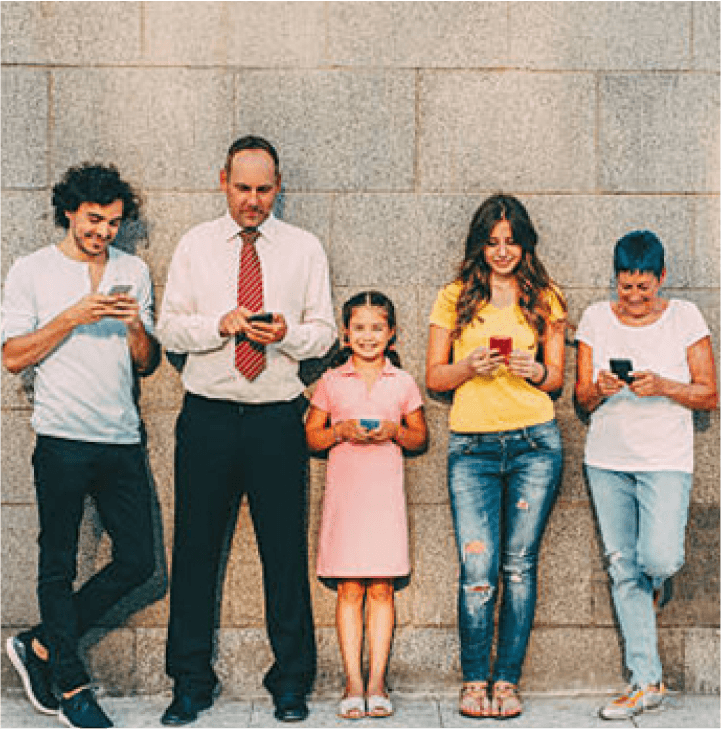

A combination of variables, including greater life expectancy, delayed retirement, and shifting career expectations, is driving the presence of five generations of workers in the economy. This tendency is expected to continue as the workforce grows more diverse and companies adjust to the requirements and tastes of various generations.
Five generations of workers
Advances in medical technology, advances in public health, and changes in lifestyle and food all contribute to longer lives. This trend is anticipated to continue as science and medicine make advances in the treatment and prevention of age-related disorders, allowing people to live longer and healthier lives.
Increased lifespan
Technological Unemployment
Urbanization

A confluence of factors, including higher life expectancy, decreased birth rates, and the aging of the baby boomer generation, is driving the aging population. This trend is expected to continue as more nations face demographic upheavals as populations age, posing new difficulties and possibilities for healthcare, social services, and the economy.
Aging population

Generational divides are an unavoidable driver of social change. Unique experiences, technology, and ideals influence each generation, resulting in individual viewpoints and actions. These differences may cause disagreements and misunderstandings, but they can also provide chances for creativity and advancement via varied viewpoints and methods.
Generational Differences
Emerging Middle class

Economic development, urbanization, and advancements in education and healthcare are driving the rise of a global middle class. This trend is expected to continue as more individuals reach the middle class throughout the globe, opening up new possibilities for companies, consumers, and society as a whole.
Rising energy demand

Population expansion, economic development, and the increased usage of energy-intensive technology are driving up energy consumption. This trend is predicted to continue as global energy demand rises, increasing pressure to create sustainable and efficient energy sources to fulfill the world's expanding energy demands.
Generation Z

The emergence of Generation Z is driven by changing demographics, advancements in technology, and evolving social and cultural norms. This trend is likely to continue as the youngest generation comes of age, bringing with them new perspectives, values, and expectations that will shape the future of society and the workforce.
Reverse Brain Drain

A variety of causes are driving reverse brain drain, including improved economic possibilities in developing nations, a rising demand for qualified individuals in emerging markets, and changing views regarding career and lifestyle. This trend is expected to continue as more highly trained employees seek new opportunities and contribute to their home nations' growth.







